Scientific papers
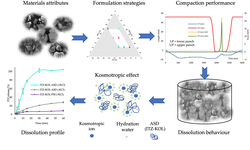
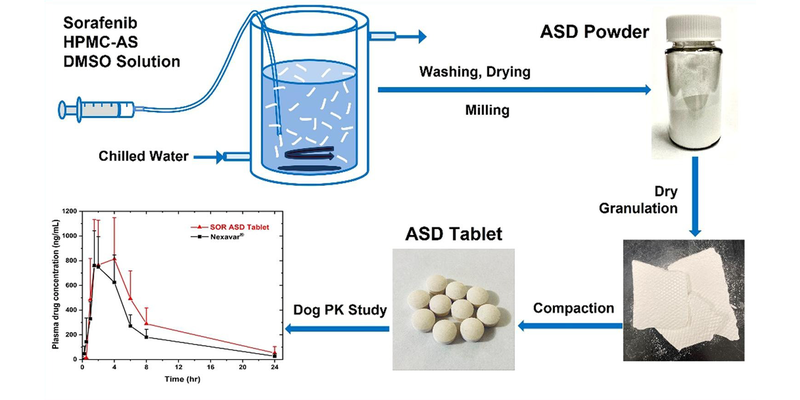
A hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMC-AS) amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) of sorafenib (SOR), prepared through coprecipitation, was utilized for the development of an immediate release tablet with enhanced oral bioavailability. The chosen ASD, featuring 40% drug loading with HPMC-AS (M grade), demonstrated superior physical stability and improved dissolution properties. The selection of the dry granulation process was based on a systematic characterization of powder properties to address the poor flowability of the ASD.
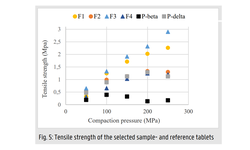
The tablet formulation was designed and evaluated using an efficient and material-sparing approach to optimize compaction conditions for manufacturing ASD tablets with low friability and rapid disintegration. The resulting SOR ASD tablets displayed approximately 50% higher relative bioavailability in dogs compared to the marketed SOR tablet product, Nexavar®.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment