Scientific papers
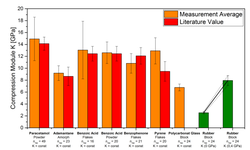
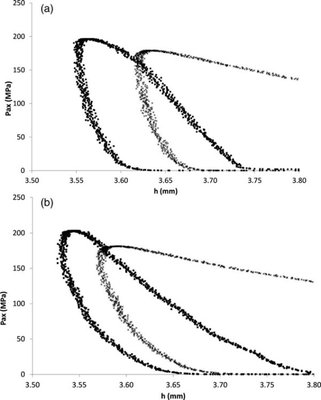
The compaction process heavily relies on the elastic properties of pharmaceutical powders. Young's modulus (E) and Poisson's ratio (v) are key parameters representing the elastic behavior. However, as the powder bed density changes during compaction, it becomes crucial to determine the moduli in relation to porosity. This research introduces a novel approach to ascertain E and v as functions of porosity through double compaction in an instrumented compaction simulator. Precompression is employed to shape the compact, with elastic properties measured at the onset of the main compaction. By monitoring axial and radial pressure, along with powder bed thickness, E and v can be established as functions of porosity. Two excipients, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and anhydrous calcium phosphate (aCP), were examined. The measured E values closely align with those from the traditional three-point bending test. Poisson's ratio for aCP was approximately 0.24, exhibiting minimal variations with porosity, while for MCC, it increased from 0.23 to 0.38 with decreasing porosity. Therefore, the conventional assumption of a 0.3 ν value for pharmaceutical powders should be approached cautiously.
Comments
No comments posted yet.
Add a comment